Creating CTXCAT Sub-indexes
An online auction site that must store item descriptions, prices and bid-close dates for ordered look-up provides a good example for creating a CTXCAT index.
Figure 3-3 Auction Table Schema and CTXCAT Index
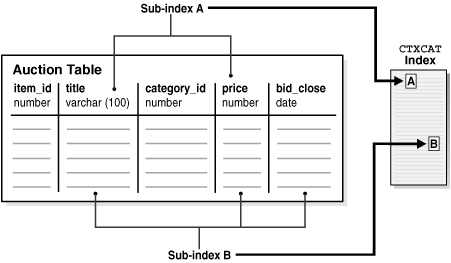
Description of "Figure 3-3 Auction Table Schema and CTXCAT Index"
Figure 3-3 shows a table called AUCTION with the following schema:
create table auction( item_id number, title varchar2(100), category_id number, price number, bid_close date);
To create your sub-indexes, create an index set to contain them:
begin
ctx_ddl.create_index_set('auction_iset');
end;
Next, determine the structured queries your application is likely to enter. The CATSEARCH query operator takes a mandatory text clause and optional structured clause.
In our example, this means all queries include a clause for the title column which is the text column.
Assume that the structured clauses fall into the following categories:
| Structured Clauses | Sub-index Definition to Serve Query | Category |
|---|---|---|
|
'price < 200' 'price = 150' 'order by price' |
'price' |
A |
|
'price = 100 order by bid_close' 'order by price, bid_close' |
'price, bid_close' |
B |
Structured Query Clause Category A
The structured query clause contains an expression for only the price column as follows:
SELECT FROM auction WHERE CATSEARCH(title, 'camera', 'price < 200')> 0; SELECT FROM auction WHERE CATSEARCH(title, 'camera', 'price = 150')> 0; SELECT FROM auction WHERE CATSEARCH(title, 'camera', 'order by price')> 0;
These queries can be served using sub-index B, but for efficiency you can also create a sub-index only on price, which we call sub-index A:
begin
ctx_ddl.add_index('auction_iset','price'); /* sub-index A */
end;
Structured Query Clause Category B
The structured query clause includes an equivalence expression for price ordered by bid_close, and an expression for ordering by price and bid_close in that order:
SELECT FROM auction WHERE CATSEARCH( title, 'camera','price = 100 ORDER BY bid_close')> 0; SELECT FROM auction WHERE CATSEARCH( title, 'camera','order by price, bid_close')> 0;
These queries can be served with a sub-index defined as follows:
begin
ctx_ddl.add_index('auction_iset','price, bid_close'); /* sub-index B */
end;
Like a combined b-tree index, the column order you specify with CTX_DDL.ADD_INDEX affects the efficiency and viability of the index scan Oracle Text uses to serve specific queries. For example, if two structured columns p and q have a b-tree index specified as 'p,q', Oracle Text cannot scan this index to sort 'ORDER BY q,p'.